IIM Researchers Find Ways to Self-assemble and Obtain Au Nanorods at Liquid/Liquid Interface
|
Liquid interfacial self-assembly of metal nanoparticles holds great promise for various applications, such as tunable optical devices, plasmonics, sensors, and catalysis. However, construction of large area ordered anisotropic nanoparticles monolayer and acquisition of self-assembled interface film are still significant challenges.
Recently, researchers developed a rapid and valid method to fabricate large-scale close packed nanomaterials at the cyclohexane/water interface in which Au nanorods (AuNRs) self-assembled into densely packed two dimensional (2D) arrays by regulating the surface ligand and suitable inducer.
In a paper published in Chemistry - A European Journal (http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/), the study team jointly led by Prof. YANG Liangbao from Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed a rapid and effective strategy to self-assemble gold nanoparticles at liquid/liquid interface and acquire integrated interfacial film.
More importantly, researchers develop a general and facile novel technique to transfer interfacial monolayer through a designed reaction cell in situ linked a microfluidic chip. Then the self-assembled nanofilm could automatically settle on the substrate and directly detect on the reaction cell in situ by portable Raman spectrometer.
Moreover, close-packed monolayer of self-assembled AuNRs gives massive efficient hotspots to create great surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) enhancement, providing high sensitivity and reproducibility as the SERS-active substrate.
Furthermore, this strategy was exploited to detect drug molecules in human urine for cyclohexane extracted targets acting as oil phase to form oil/water interface.
Universal platform, handy tool and fast pretreatment of this strategy ensure a good capability for drug detection in complicated biological system,and the stategy even showed great promise in the issue of rapid, credible and on-spot detection for drug crimes.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (21505138 and 21571180), Special Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016T90590), the Anhui Natural Science Foundation (1508085MB26), the Sci-tech Police Project of Anhui Province (1704d0802186), the CASHIPS Director’s Fund (YZJJ201701) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M622031).
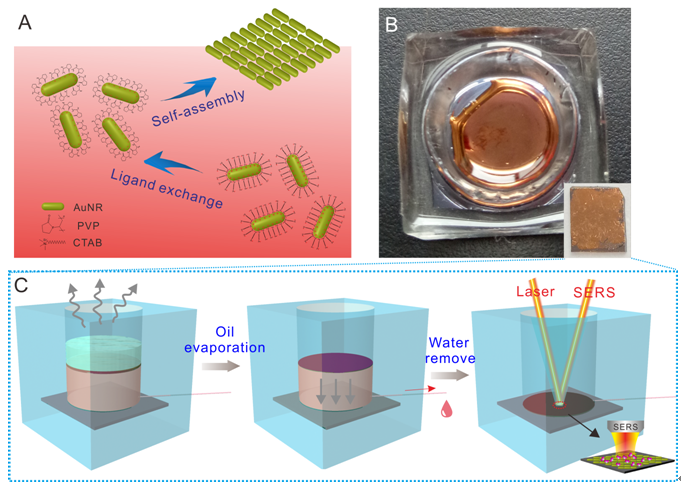
Figure. Self-assembly of AuNRs at liquid interface. Schematic illustrations and optical images of the A) ligand exchange of AuNRs, B) acquired interfacial film, C) natural deposition strategy to obtain the self-assembled film. (Image provided by MAO Mei)
Article link: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/chem.201705700/full
Title: Natural deposition strategy of interfacial self-assembled large-scale densely packed monolayer film with ligand exchanged Au nanorods for in situ SERS drugs detection
Key words: SERS; AuNRs; self-assembly; liquid interface; drug
Contact:
Prof. YANG Liangbao, Ph. D
Institute of Intelligent Machines, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.iim.cas.cn/) Hefei, Anhui 230000, China
Tel: 86-551-6559-2385
