Chinese researchers realized highly selective and sensitive detection of Pb(II) that is very hard to sense accurately for the mutual interference among the different heavy metal ions.
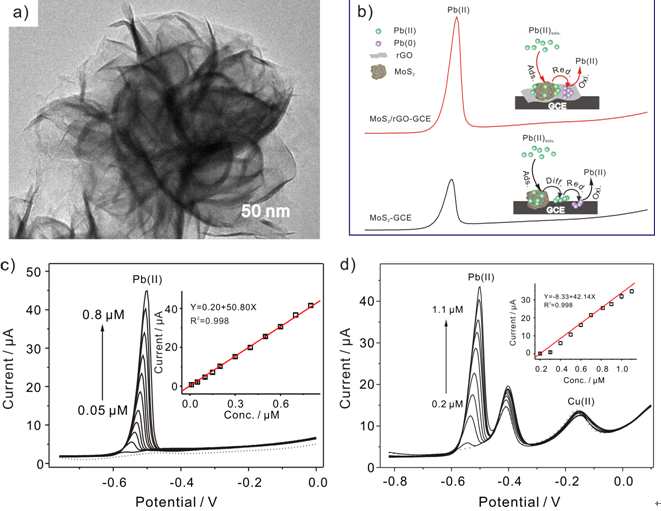
The team made flower-like MoS2/rGO composite with ultra-thin nanosheets to overcome problems in the detection and managed to achieve high performance selective and sensitive sensing of Pb(II).
Actually, electrochemical analytical tools have been widely used to detect Pb(II), and through which achievements have been made. However, the mutual interference among the different heavy metal ions is serious due to the inter-metallic compounds formed among them and the competition for the active sites at the modified electrode surface.
Therefore, it is still a challenge, we have to face, to accurately detect real water samples contaminated by Pb(II) with interference by coexisting heavy metal ions.
In the recent study, the team found that MoS2/rGO nanocomposite presented highest adsorption capacity for Pb(II), which enabled its modified electrode to realize the selective and sensitive detection of Pb(II).
To further test, they performed their method in realwater environment. According to the test with the waste water collected from sewage disposal plant in the local community, the team obtained the good that was in accordance with it in the lab.
Moreover, the teamalso took a closer look at the interference among the coexisting ions and they uncovered differe-nce in the ablility of MoS2/rGO nanocomposite to absorb differentions.
This work was supported by the postdoctoral innovation talents supporting project (BX20180311), the national natu-ral science foundation of China(21735005), the technology major project of Anhui Province(17030801033), and the natural science foundation of Anhui Province (1708085MB36), the postdoctoral researcher funding project of Anhui Province (2018B244).