Removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions has drawn more and more attentions in recently years due to the serious global health challenge they brings to human society. To solve the heavy metal pollutions, it is of great significance to develop robust and effective purification processes of wastewaters contaminated by heavy metals.
A mass of water treatment technologies have been developed and utilized to remove heavy metals. Among them, adsorption is a kind of safe method with high effectiveness and low cost, However, there are still some unresolved problems associated with their applications, and one of the most serious problems is the low adsorption rate. Most of the adsorbents take a while to get equilibrium. therefore, to develop adsorbents with high adsorption rate at present is an urgent necessity.
Prof. LIU Jinhuai and Asso. Prof. KONG Lingtao’s joint team of Institute of Intelligent Machines(IIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), successfully developed a new kind of adsorbent to rapidly remove heavy metals from drinking water.
β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) polymers crosslinked with rigid aromatic groups are prepared and used for lead (Pb), copper (Cu) and cadmium (Cd) removal for the first time. The negatively charged β-CD polymers with large BET surface area are suitable to be used in heavy metal adsorption. The adsorption process is completed in 5 mins, which is much shorter than most of the adsorbents. The maximum of adsorption capacities at 25 ºC for Pb, Cu and Cd are 196.42, 164.43 and 136.43 mg/g when the initial concentration is 200 mg/L. The adsorption process on the surface of β-CD polymer is an endothermic and spontaneous process. Both of the electrostatic interaction and distribution of Pb, Cu and Cd species influence the adsorption process with different pH values. The order of removal efficiencies in multi-component adsorption for the three metal ions are Pb > Cu > Cd. The adsorption mechanisms are H+ ions on hydroxyl groups exchanged with heavy metal ions and electrostatic interactions.
These results demonstrate that the β-CD polymers could be developed into effective adsorbents for rapid removal of heavy metals. Meanwhile, this work is meaningful for achieving rapid removal of heavy metals in the later works.
This work is supported by the National Key Scientific Program-Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (Grant No.2011CB933700), the CASHIPS Director's Fund (Grant No.YZJJ201617), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21177131, 61273066, 11205204, 21105001, 21077106, and 61104205).
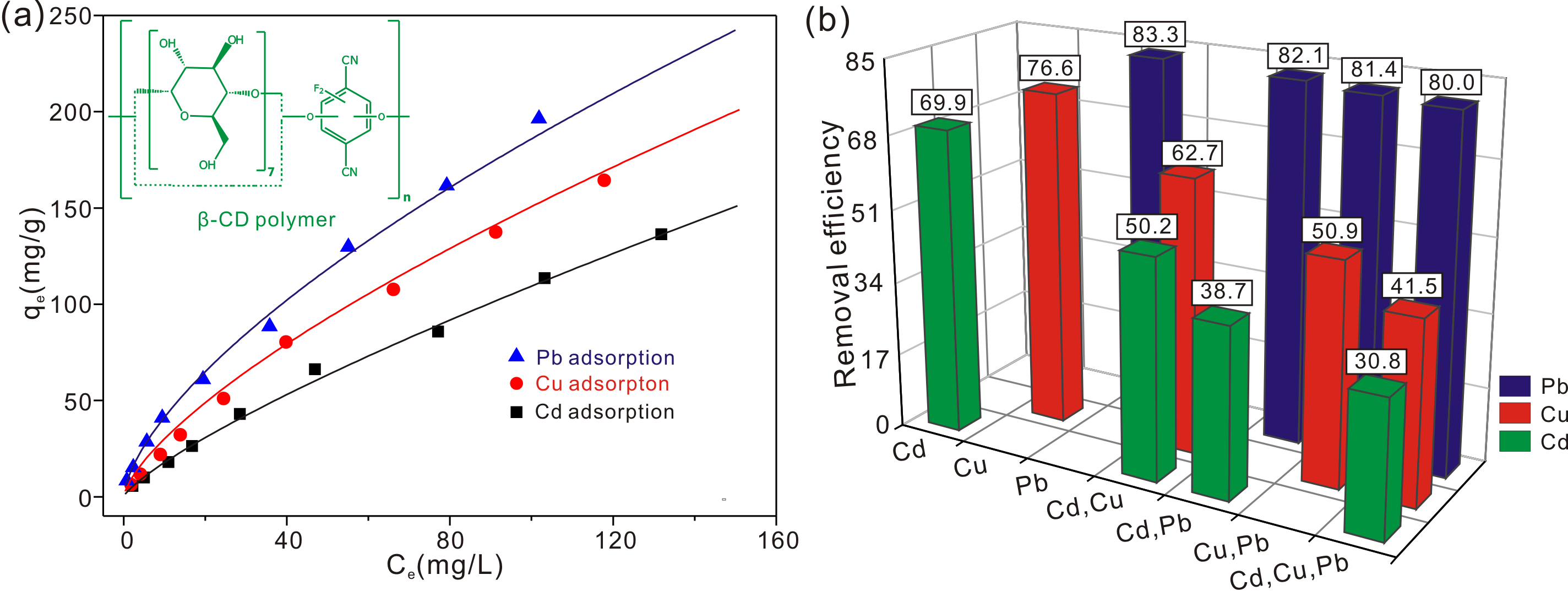
Figure. The single-component (a) and multi-component (b) adsorption behavior of β-cyclodextrin polymers for Pb, Cu and Cd.
Article link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169433217320974
Title: Rapid adsorption of Pb, Cu and Cd from aqueous solutions by β-cyclodextrin polymers.
Key words: β-CD polymer, heavy metals, adsorption, pH effects, mechanism
Contact:
Asso. Prof. KONG Lingtao, Institute of Intelligent Machines, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.iim.cas.cn/) Hefei, Anhui 230000, China
Tel: 86-551-6559-2420
E-mail address: ltkong@iim.ac.cn
Image provided by HE Junyong
