Electrochemical analytical tools have been widely investigated for toxic As(III) detection and the achievements have also been very fruitful. However, a truth was ignored during the measurements arsenic with electrochemical method, i.e., the speciation of arsenic is different at different pH values, which could affect the accuracy of arsenic detection.
Therefore, with the consideration of the change of As(III) speciation in different pH conditions, developing a reliable method for the detection of As(III) in nearly natural water pH is meaningful for practical applications.
Recently, a study team led by Prof. HUANG Xingjiu in Institute of Intelligent Machines (IIM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, explored the electrochemical detection of arsenic(III) in nearly natural water pH by using nanocomposite of hierarchically porous CeO2-ZrO2 nanospheres decorated with ∼10 nm Au nanoparticles. The paper has been accepted for publication by Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/09254005
In this work, overcoming the change of arsenic(III) speciation at different pH conditions, a new nanocomposite of hierarchically porousCeO2-ZrO2nanospheres decorated with ∼10 nm AuNPs (AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2)has been found to be used for reliable detection of ultratrace original As(III) speciation in nearly natural water pH (pH 8.0).
Moreover, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results quantificationally reveal the largest amount of adsorbed As(III) on the AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2 nanocomposite in nearly natural water pH. Accordingly, such a nanocomposite works based on a strategy combined the excellent adsorption of hierarchically porous CeO2-ZrO2 nanospheres with robust electrocatalytic ability of decorated ∼10nm AuNPs.
Considering its improved sensitivity, limit of detection, ultrahigh anti-interference ability and the property that As(III) can maintain the original speciation in nearly natural water pH, AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2 nanocomposite is expected to be more accurate and reliable for online monitoring of As(III) in real water samples.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21475133, U1532123, 21377131, U1432131, 21645006 and U1532120), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1708085MB36), and the youth project of National Natural Science Fund (11405256). X.-J. Huang acknowledges the CAS Interdisciplinary Innovation Team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the CASHIPS Director’s Fund, Grant No. YZJJ201701, for financial support.

Figure 1. a) SEM and TEM images of the AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2 nanocomposite.b) Typical SWASV responses of AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2/GCE toward As(III) in pH 8.0 HAc-NaAc buffer solution. c) The corresponding linear equation of the stripping current (squares) and As(III) concentration. The columns represent the corresponding peak area of different concentration of As(III). d)High-resolution XPS spectra of As3d signature region for AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2 after As(III) absorption at different pH media.
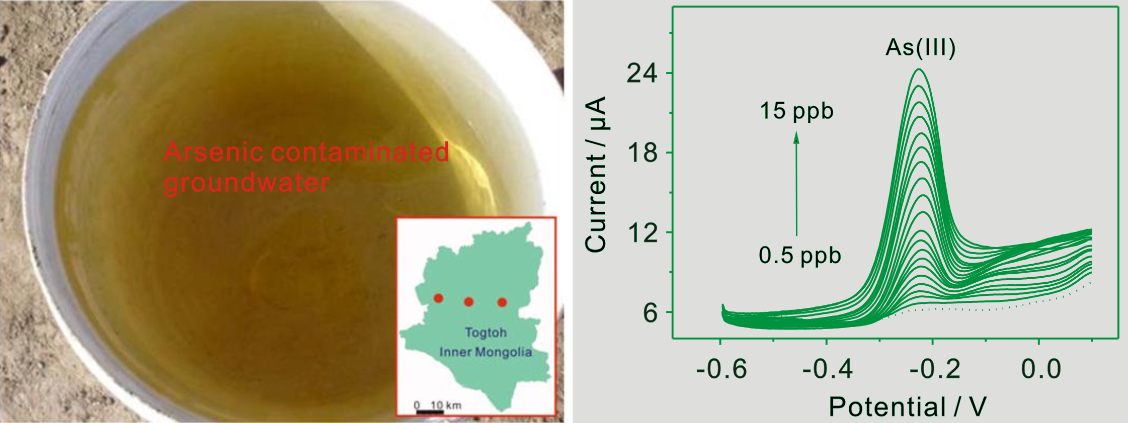
Figure 2. Arsenic contaminated groundwater in Togtoh region of Inner Mongolia, and electrochemical detection of arsenic(III)
Key words:electroanalysis; arsenic(III); AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2; nearly groundwater pH
Articlelink:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925400517314181
Title: Reliable electrochemical sensing arsenic(III) in nearly groundwater pH based on efficient adsorption and excellent electrocatalytic ability of AuNPs/CeO2-ZrO2 nanocomposite
Contact:
Prof. HUANG Xing-Jiu, Ph. DPrincipal Investigator
Institute of Intelligent Machines, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
Tel: 86-551-6559-1167
Email: xingjiuhuang@iim.ac.cn
