Arsenic is considered to be one of the most toxic element in the natural environment. With the development of nanotechnology, nanomaterials are increasingly being used to modify and improve the analytical performance of various electrodes, and the latest achievements in regards to arsenic detection have been fruitful.
Therefore, a concise and updated review is considered timely to evaluate the progress, follow up on the development trends, and identify the key issues on the electrochemical determination of arsenic.
Aiming at this, recently, a study team led by Prof. HUANG Xingjiu in Institute of Intelligent Machines (IIM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, studied the current situation and the most important developments in the electrochemical determination of arsenic within the last 2 years.
The paper has been accepted for publication by Current Opinion in Electrochemistry. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/24519103
In the review, electrode materials, electrolyte pH and recent technical advances on the determination of arsenic within the last 2 years are summarized.
These studies mainly focus on the detection of arsenic at modified electrodes consisting mostly of gold and alloy nanostructures, metal oxide nanostructures, graphene and organic group functionalized nanomaterials.
Few observations, schematically presented in Figure 1, can be made: 1- all studies are reporting modified electrodes, mostly made of gold or alloy nanostructures, but still, a clear trend in trying to get away from noble materials start to emerge with the use of metal oxide nanostructures, graphene or other functionalized materials; 2- although acidic conditions are by far the most common studies where detection is made at neutral pH or in alkaline conditions are increasing; 3- few studies have reported the integrated/on-line coupling of electrochemical methods with other techniques.
In addition, key issues and remaining challenges that require further attention for a successful electrochemical detection of arsenic are proposed.
Any advances in understanding or sensor performance contribute to the development of robust, easy-to-use, reliable and sensitive sensor that can ideally be used on-site (at the point of sampling) or in-situ (directly in the water column) for automated monitoring of arsenic by non-specialist end-users. For the worldwide problem of arsenic, such sensor would be very much welcome indeed.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61474122, 31571567, 61106012, 21377131, 21475133, and U1532123). X.-J. Huang acknowledges the CAS Interdisciplinary Innovation Team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, for financial support.
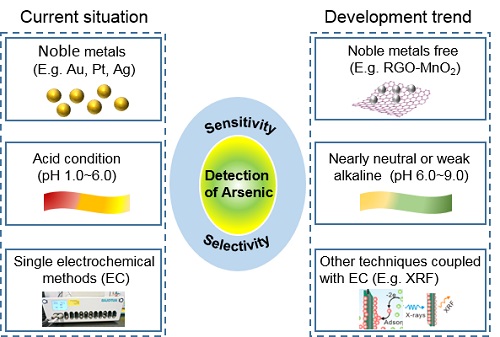
Figure 1. Current situation and development trend of arsenic detection by using
electrochemical methods.(Image provided by YANG Meng)
Article link:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2451910317300273
Title:Recent developments in electrochemical determination of arsenic
Key words: electrochemicaldetermination; arsenic; development trends
Prof. HUANG Xing-Jiu, Ph. D, Principal Investigator
Institute of Intelligent Machines, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
Tel: 86-551-6559-1167
Email: xingjiuhuang@iim.ac.cn
